Secondary ion mass spectrometry: Difference between revisions
From Mass Spec Terms
No edit summary |
gallery |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
|ref=A. Benninghoven, B. Hagenhoff, E. Niehuis. Anal. Chem. 65, 630A (1993). | |ref=A. Benninghoven, B. Hagenhoff, E. Niehuis. Anal. Chem. 65, 630A (1993). | ||
}} | }} | ||
==Gallery== | |||
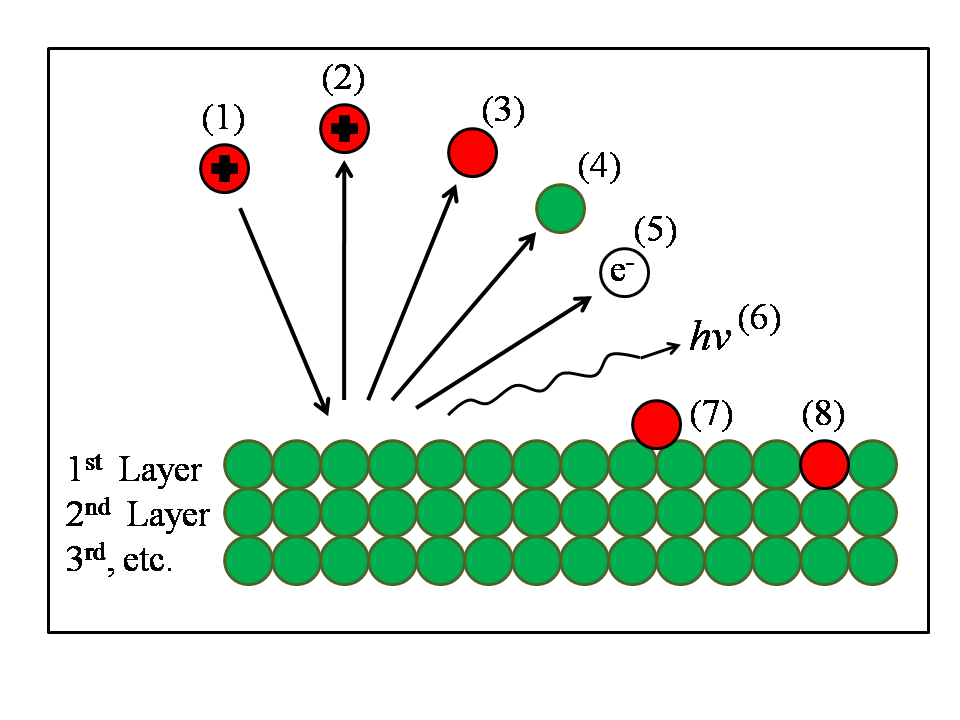
{{gallery|file=File:Ion surface interactions.gif|caption=Overview of various ion-surface interactions. (1)-incoming ion; (2)-scattering; (3)-neutralization and scattering; (4)-sputtering or recoiling; (5)-electron emission; (6)-photon emission; (7)-adsorption; (8)-displacement, e.g. from sputtering event.}} | |||
[[Category:Ionization]] | [[Category:Ionization]] | ||
Revision as of 12:58, 5 July 2025
| IUPAC RECOMMENDATIONS 2013 |
| Secondary ion mass spectrometry |
|---|
| Technique in which a focused beam of primary ions produces secondary ions by sputtering from a solid surface. The secondary ions are analyzed by mass spectrometry. |
| Related Term(s): dynamic secondary ion mass spectrometry (DSIMS) |
| Reference(s):
A. Benninghoven, B. Hagenhoff, E. Niehuis. Anal. Chem. 65, 630A (1993). |
| From Definitions of Terms Relating to Mass Spectrometry (IUPAC Recommendations 2013); DOI: 10.1351/PAC-REC-06-04-06 © IUPAC 2013. |
Gallery